What Is FIP in Plumbing? A Completed Guide 2026
_1764135646_WNo_1600d900.webp)
Introduction
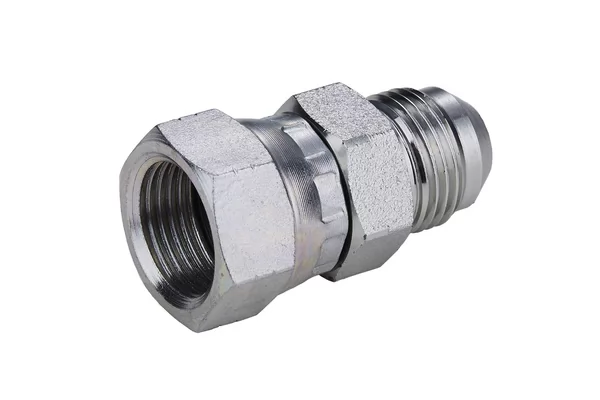
In hydraulic systems, industrial process piping, and OEM fluid power applications, accurate specification of threaded connections is non-negotiable. One of the most frequently referenced — and occasionally misunderstood — designations is FIP (Female Iron Pipe).
FIP refers to female tapered pipe threads conforming to the ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 NPT (National Pipe Taper) standard. These are internal threads designed to accept male NPT or NPTF threaded components, providing a pressure-tight mechanical seal when properly assembled with thread sealant or anaerobic compounds.
Although the term originated with iron and steel pipe, modern FIP threads appear across a wide range of materials including 316/316L stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and specialty alloys — materials routinely specified in hydraulic power units, test stands, refineries, and high-purity gas delivery systems.
For procurement engineers and system designers, understanding the precise meaning of “FIP” eliminates costly mismatches between drawings, BOMs, and delivered components.
What Is FIP in Plumbing?
FIP (Female Iron Pipe) refers to a female tapered pipe thread that follows the ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 NPT standard. It is designed to mate with male NPT or NPTF threads, forming a pressure-tight seal through thread interference and sealant. FIP threads are widely used in plumbing, hydraulic, gas, and industrial piping systems.
FIP in Plumbing vs Hydraulic Systems: Key Differences
| Aspect | Plumbing Systems | Hydraulic Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Pressure | Below 20 bar | 250–700 bar |
| Common Thread Type | FIP (NPT) | FIP (NPTF Dryseal) |
| Sealant Use | PTFE tape common | Anaerobic or no sealant |
| Failure Risk | Minor leakage | Safety-critical |
FIP vs MIP: Critical Distinctions in Industrial Specifications
| Parameter | FIP (Female Iron Pipe) | MIP (Male Iron Pipe) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread location | Internal (inside fitting) | External (outside nipple or adapter) |
| Mates with | MIP or MNPT external threads | FIP or FNPT internal threads |
| Typical components | Female threaded elbows, tees, couplings, valves, gauges | Threaded nipples, plugs, male adapters |
| Pressure rating impact | Same rating as mating male thread when correctly sealed | Same rating as mating female thread |
In hydraulic manifolds and valve assemblies, correct pairing of FIP and MIP ends is essential for maintaining rated burst pressures and avoiding cross-threading during assembly.
How to Read FIP Thread Callouts on Engineering Drawings
On engineering drawings and purchase orders, FIP threads may appear under several equivalent designations. Misinterpreting these callouts is a common cause of procurement errors.
- 1/2" FIP = 1/2" FNPT (female tapered pipe)
- FIP (NPT) = female ASME B1.20.1 thread
- FIP-NPTF or FNPTF = female Dryseal thread per SAE J476
Unless otherwise specified, most North American drawings interpret “FIP” as standard female NPT.
FIP vs NPT vs NPTF: Clearing Up Decades of Industry Confusion
This is where most catalog descriptions fall short.
- NPT (ANSI/ASME B1.20.1) – Standard tapered pipe thread requiring thread sealant (PTFE tape or pipe dope)
- NPTF (SAE J476, also called Dryseal) – Modified taper with tighter root/crest tolerances; achieves metal-to-metal seal without sealant in many cases
- FIP/FNPT – Trade terminology indicating the female version of the above standards
In practice:
- When a drawing simply says “1/2" FIP”, North American manufacturers interpret it as female NPT
- When Class 2500–6000 psi hydraulic or fuel systems are involved, engineers typically specify NPTF female (still commonly labeled as “FIP” in catalogs) for superior sealing and galling resistance
Leading hydraulic fitting manufacturer, including HGW Hydraulic, offer both standard NPT and SAE-certified NPTF female threads in 304/316 stainless and A105 carbon steel to meet diverse application requirements.
FIP Thread Standards, Taper Angles, and Complete Dimension Reference
All FIP threads sold in North America follow one of two standards:
| Standard | Full Name | Taper Angle | Seal Method | Typical Max Pressure (316SS, Class 3000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | National Pipe Taper (ASME B1.20.1) | 1°47′ | Requires sealant | 4000–5000 psi (275–345 bar) |
| NPTF | National Pipe Taper Fuel (SAE J476) | 1°47′ | Dryseal – often no sealant | 6000–10,000 psi (414–690 bar) |
Complete FIP / NPT / NPTF Size & Thread Data Table (most competitors only give 3–4 sizes; we give all common sizes that procurement actually uses)
| Nominal Size | Threads Per Inch (TPI) | Thread OD Male (in) | Thread ID Female (in) | Pitch Diameter at End (E1) | Max Working Pressure 316SS Class 3000 (psi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/16″ | 27 | 0.3125 | 0.276 | 0.281 | 9,000 |
| 1/8″ | 27 | 0.405 | 0.369 | 0.374 | 6,500 |
| 1/4″ | 18 | 0.540 | 0.492 | 0.502 | 6,500 |
| 3/8″ | 18 | 0.675 | 0.627 | 0.637 | 5,500 |
| 1/2″ | 14 | 0.840 | 0.782 | 0.792 | 5,500 |
| 3/4″ | 14 | 1.050 | 0.992 | 1.002 | 5,000 |
| 1″ | 11.5 | 1.315 | 1.243 | 1.256 | 4,500 |
| 1-1/4″ | 11.5 | 1.660 | 1.583 | 1.596 | 4,000 |
| 1-1/2″ | 11.5 | 1.900 | 1.822 | 1.835 | 4,000 |
| 2″ | 11.5 | 2.375 | 2.285 | 2.298 | 3,500 |
| 2-1/2″ | 8 | 2.875 | 2.761 | 2.786 | 4,000 |
| 3″ | 8 | 3.500 | 3.376 | 3.401 | 3,800 |
Data source: ASME B1.20.1-2013 & SAE J476; pressure values based on HGW Hydraulic internal testing + third-party burst reports.
How to Positively Identify FIP Threads in the Field or Incoming Inspection
Procurement and QC departments use these four methods (in order of speed):
1. Thread Gauge (Go/No-Go)
Fastest and most reliable. HGW Hydraulic includes calibrated NPT/NPTF plug gauges with every 500+ piece order.
2. Visual + Tactile Check
- FIP = internal threads only
- Taper is visible: the thread crests get progressively smaller toward the face
- NPTF crests appear slightly crushed/truncated compared to NPT
3. Optical Comparator or Thread Profile Projector
Required for ISO 9001 / IATF 16949 incoming inspection when full traceability is mandatory.
4. Pitch Diameter Measurement with Thread Wires
Used when customer drawing specifies “NPTF Class 2” tolerance.
FIP Materials Selection for Industrial & Hydraulic Applications
| Material | Common Grades | Max Temp | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications | Lead Content | Price Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel A105 | Forged | 425°C | Poor (needs plating) | General hydraulic, oil & gas | <0.35% | 1.0× |
| 316/316L Stainless | ASTM A182 F316/316L | 540°C | Excellent | Food, pharma, offshore, CNG | <0.03% | 4.2× |
| Duplex 2205 / 2507 | ASTM A182 F51/F53 | 600°C | Outstanding | Desalination, high-chloride service | <0.03% | 7.5× |
| Brass CA377 / C37700 | Forged | 150°C | Good | Compressed air, low-pressure water | 2.5–3.7% | 2.1× |
| Monel 400 / K500 | ASTM SB564 | 480°C | Superb in seawater | Marine hydraulic, subsea control lines | Nil | 12×+ |
| 6-Moly (AL-6XN, 254SMO) | UNS N08367 | 600°C | Extreme pitting resist | Chlor-alkali, flue gas desulfurization | Nil | 15×+ |
HGW Hydraulic standard stock program maintains over 180 SKUs of 316/316L Class 3000 and 6000 FIP fittings with EN 10204 3.1 certificates ready for immediate dispatch.
FIP in High-Pressure Hydraulic Systems: Why Serious Applications Move to NPTF (Dryseal)
Standard NPT was never designed for 700 bar mobile hydraulics or 99.999% helium leak-tight instrument lines.
NPTF advantages in real-world hydraulic service:
- Interfering crest/root contact creates primary metal-to-metal seal
- Reduced sealant contamination risk (critical in oxygen and hydrogen systems)
- Galling resistance increased 300–400% in stainless steel
- Tested to 4× working pressure without leakage in HGW laboratory
Case study: A North American OEM of 700-bar hydraulic test benches switched from NPT to NPTF female ports after experiencing 4% field leakage rate. Post-switch failure rate dropped to 0.03% across 42,000 manifolds.
FIP Application Scenarios in Industrial & Hydraulic Systems (With Real Project References)
| Application | Typical Size | Material Preference | Pressure/Temp | Why FIP is Specified |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic power unit manifold ports | 1/4″–1″ | 316SS NPTF Class 6000 | 400–700 bar, –40~120°C | Compact footprint, field-replaceable valves |
| Instrument air headers | 1/8″–1/2″ | 316SS or Brass | 10–20 bar | Legacy drawings, millions of existing FIP take-offs |
| CNG dispensing stations | 1/4″–1″ | 316L NPTF | 250–350 bar | Fast make/break during dispenser maintenance |
| Offshore firewater deluge valves | 1″–2″ | Duplex 2205 | 15–25 bar seawater | Corrosion resistance + compatibility with existing carbon-steel piping |
| High-purity nitrogen purge panels | 1/4″–1/2″ | Electropolished 316L | 5–150 bar | No PTFE tape allowed → NPTF Dryseal required |
| Mobile hydraulic test benches | 1/4″–3/4″ | Carbon steel Cr13 coating | 700 bar cyclic | Cost-effective + proven fatigue life with NPTF |
Comprehensive Compatibility Matrix: FIP with Global Thread Standards
| Female Thread | Male Thread Counterpart | Seal Method | Compatibility Notes | Typical Cross Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIP (NPT) | NPT, NPTF, NPSM | Sealant required | 100% compatible | — |
| FIP (NPTF) | NPTF only | Dryseal primary | NPT male acceptable but loses Dryseal benefit | SAE AS71051 |
| FIP (NPT) | BSPT (R) | Sealant | Limited (1–2 turns engagement only) → high leak risk → not recommended | — |
| FIP (NPT) | BSPP (G) | Washer or O-ring | Not compatible without special BSPP male with 60° cone + bonded washer | — |
| FIP (NPT) | JIC 37° | Never | Completely different flare → catastrophic failure if forced | — |
| FIP (NPT) | SAE ORB (O-ring Boss) | Never | Different thread form and seal method | — |
| FIP (NPT) | DIN 3852 Form A/B | Sealant | Metric taper different → not interchangeable | — |
| FIP (NPT) | Metric ISO 6149 | O-ring | Not compatible | — |
Rule of thumb for procurement: Never mix imperial tapered with metric or parallel standards without an explicitly tested adapter.
Top 5 Costly Mistakes When Specifying or Purchasing FIP Fittings
1. Accepting “NPT” when the system actually demands NPTF Dryseal
→ Result: field leakage in oxygen-clean or high-cycle applications
→ Cost: $80,000–$350,000 per shutdown incident
2. Confusing nominal size with actual thread OD
→ 1/2″ FIP is NOT 0.500″ OD (actual ≈0.840″) → wrong hole drilled in manifolds
3. Ordering Schedule 40 fittings for 500+ bar service
→ Class 3000 or 6000 forged fittings are mandatory above 250 bar
4. Missing material traceability requirements
→ EN 10204 3.1/3.2 certificates + positive material identification (PMI) now mandatory in most offshore and pharma projects
5. Assuming all 316/316L is the same
→ Low-carbon 316L + sulfur 0.008–0.015% is required for orbital welding and galling resistance
HGW Hydraulic eliminates these risks with lot-level traceability, standard 3.1 certificates, and pre-shipment PMI on every stainless order.
Professional Selection Guidelines: When to Specify FIP and When to Move On
| Scenario | Recommended Thread | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure ≤250 bar & cost critical | Standard NPT (FIP) | Lowest cost, widely available |
| Pressure 300–700 bar or >5000 cycles | NPTF Dryseal | Superior fatigue & sealing performance |
| Clean hydraulic (NAS 6 or better) | SAE ORB or JIC preferred | NPT/F generates particles during assembly |
| Oxygen, hydrogen, or explosive decompression | NPTF + Monel or no tape | PTFE tape prohibited |
| Future maintenance by non-specialized crews | FIP/NPTF | Most field technicians carry NPT tools |
| Space-constrained manifolds | FIP/NPTF | Smallest envelope for given flow compared to flange or ORB |
Sealing Best Practices for FIP/NPTF Threads in Critical Service
| Application Class | Recommended Sealant | Wraps / Coats | Torque (ft-lb) for 316SS Class 3000 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General hydraulic | PTFE tape (yellow, high-density) | 2–3 wraps | 25–35 (1/2″) | Start second thread, clockwise, no fraying |
| High-purity gas | Loctite 577 or 567 anaerobic | 360° coverage | Hand-tight + 1.5 turns | No tape contamination |
| Oxygen service | PFA tape or Swagelok-approved oxygen paste | 1.5 wraps | Controlled torque only | BAM or EIGA approved only |
| Steam ≤150 psi | Graphite/nickel paste | 3 coats | 40–50 (1/2″) | High-temp anti-seize |
| NPTF Dryseal | None or light hydraulic oil only | — | Hand-tight + 1–2 turns | Over-torquing destroys interference seal |
HGW Hydraulic includes torque specification sheets with every Class 3000/6000 order.
Frequently Asked Questions from Procurement & Engineering Teams
Q1: Is “FIP” still an acceptable callout on 2025 engineering drawings?
A: Yes. In North America, “FIP” or “FNPT” remains universally understood as female tapered pipe thread per ASME B1.20.1. For new designs requiring Dryseal performance, specify “FIP-NPTF” or “FNPTF” plus SAE J476 reference.
Q2: What is the real pressure rating of a 1/2″ 316SS Class 3000 FIP fitting?
A: Typical working pressure is 5500–6000 psi (380–414 bar) with 4:1 safety factor. Burst exceeds 20,000 psi when assembled with matching NPTF male and proper sealant. Full test reports available from HGW Hydraulic on request.
Q3: Do you offer low-lead or lead-free FIP fittings for potable water or food contact?
A: Yes. All HGW 316/316L fittings contain <0.03% Pb and comply with NSF/ANSI 372 and FDA requirements. Brass CA377 is limited to non-potable compressed air and hydraulic service.
Q4: What is the MOQ and standard lead time for custom 2507 Duplex FIP fittings?
A: Standard MOQ is 100 pieces per size. Stock 316SS Class 3000 items ship same day; Duplex and Monel orders typically 4–6 weeks ex-works with EN 10204 3.2 + NORSOK M-650 certification available.
Q5: Can FIP ports be orbital-welded after machining?
A: Yes, provided 316L with controlled sulfur 0.008–0.015% is used and wall thickness meets ASME B31.3. HGW Hydraulic supplies weld-ready extended-leg FIP fittings specifically for automated orbital welding.
Q6: Are your FIP threads inspected 100% with go/no-go gauges?
A: Every production lot undergoes 100% go/no-go gauging plus sample pitch-diameter and taper inspection per ASME B1.20.1. Gauge certificates traceable to NIST are included with shipments over 500 pieces.
Conclusion
Specifying the correct female tapered pipe thread eliminates one of the most common sources of leakage, delays, and field rework in hydraulic and industrial piping systems. While the term “FIP” is simple, the underlying standards, material selection, pressure ratings, and sealing practices directly impact system reliability, total cost of ownership, and safety.
When performance, traceability, and delivery certainty matter, partner with a manufacturer who treats FIP threads as a precision component—not a commodity.
HGW Hydraulic maintains one of North America’s largest inventories of certified Class 3000 and 6000 316/316L and Duplex FIP fittings, with full material certificates, PMI reports, and 48-hour quotations as standard.
Need compliant, high-performance FIP solutions delivered on time? Contact our engineering sales team at sales@hgwhydraulic.com or visit www.hgw-hydraulic.com for drawings, stock list, and live inventory.
-
2025 Shanghai Bauma Exhibition China International Construction Machinery ExhibitionUpdate on 2024-12-25
-
2025 Las Vegas International Mining ExhibitionUpdate on 2024-12-25
-
Leading the High-End and Empowering the World | Bauma China 2025, Hgw Successfully ConcludedUpdate on 2024-12-25
-
Hgw's Multi-field Hydraulic Products Appeared at the Exhibition丨MINEXPOUpdate on 2024-12-25
-
2025 PTC ASIAUpdate on 2025-02-12
-
Top 10 Leading Hydraulic Fitting Companies in the World[2025 Updated]Update on 2025-02-27
-
Top 10 Global Suppliers of Hydraulic Hose FittingsUpdate on 2025-03-04
-
HGW's O-Ring Face Seal Fittings(ORFS): From Core to Best UseUpdate on 2025-03-08